Understanding Battery Capacity: A Practical MHPOWOS LiFePO₄ Guide
Share
Clear explanations of Ah, Wh, voltage, and how to choose the right MHPOWOS LiFePO₄ battery for RVs, off-grid cabins, and backup power.
What Does “Ah” Mean in a Battery?
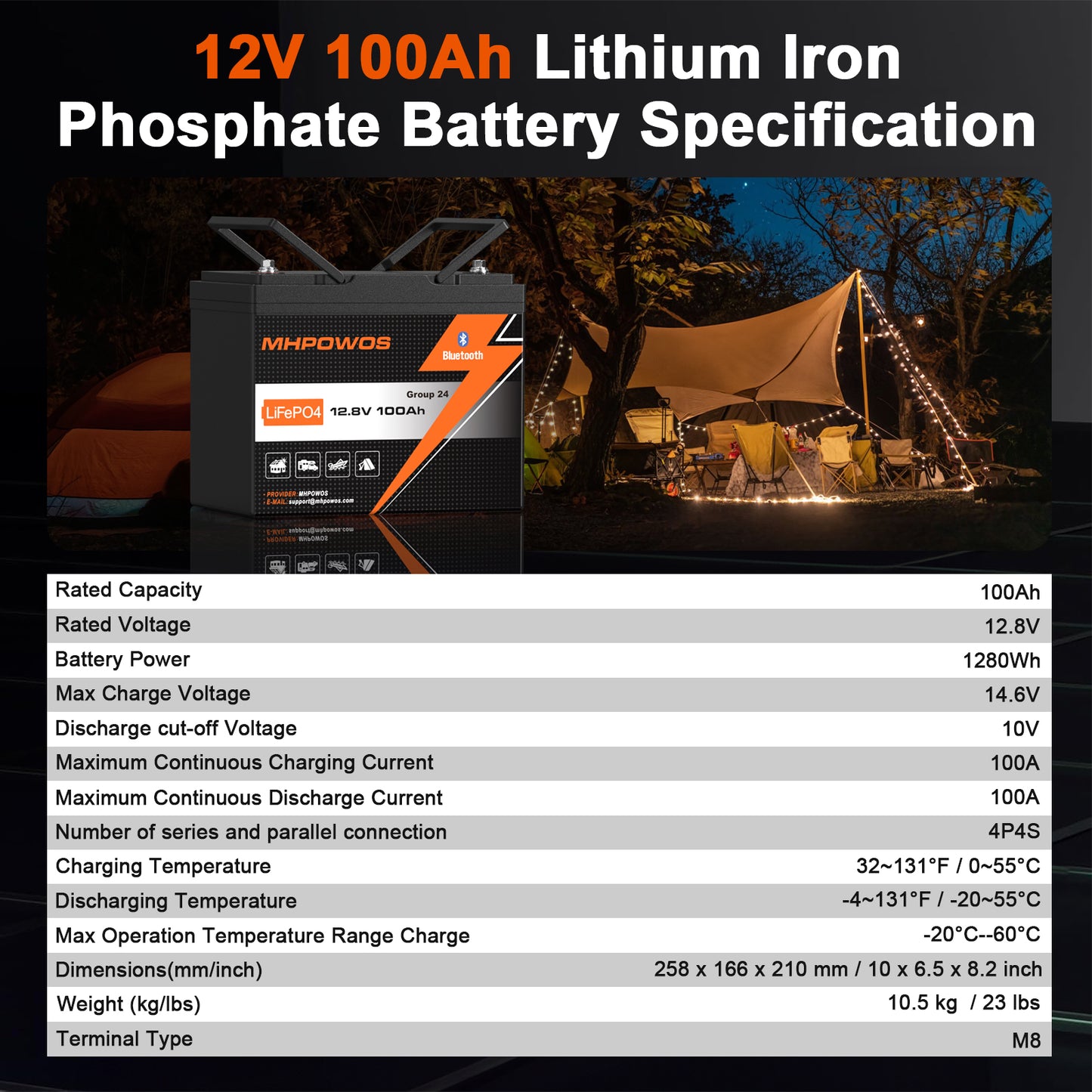
Amp-hours (Ah) is a unit that tells you how much current a battery can supply over a period of time. For example, a 12.8 V battery rated at 100 Ah can theoretically provide 100 amps for 1 hour or 10 amps for 10 hours. That said, the real usable capacity depends on discharge rate, battery chemistry, temperature, and system losses.
Tip: Ah alone doesn’t show total energy. To compare batteries, convert Ah into watt-hours (Wh) using voltage — see the next section.
Why Choose LiFePO₄ — MHPOWOS Advantages
LiFePO₄ (lithium iron phosphate) cells are popular for portable and stationary energy systems because they combine safety, durability, and performance. Compared with lead-acid, LiFePO₄ offers:
- Higher usable capacity (you can safely use a greater percentage of the rated Ah)
- Much longer cycle life (often thousands of cycles)
- Lighter weight and smaller footprint
- Stable chemistry with excellent thermal and chemical stability
MHPOWOS LiFePO₄ batteries are designed for real world use cases — RVs, off-grid cabins, portable power stations, and reliable backup systems. Browse the full lineup here: MHPOWOS LiFePO₄ collection.
How to Read Battery Ratings: Voltage × Ah = Watt-Hours (Wh)
To compare energy capacity across batteries, convert voltage and amp-hours into watt-hours:
Energy (Wh) = Voltage (V) × Amp-Hours (Ah)
Example: a 12.8 V, 100 Ah LiFePO₄ battery ≈ 1,280 Wh (1.28 kWh). When sizing a system, calculate the energy you actually need per day in Wh, then select a battery with enough usable Wh to meet that need plus reserve.
Key Factors When Choosing an MHPOWOS LiFePO₄ Battery
1. Voltage Matching
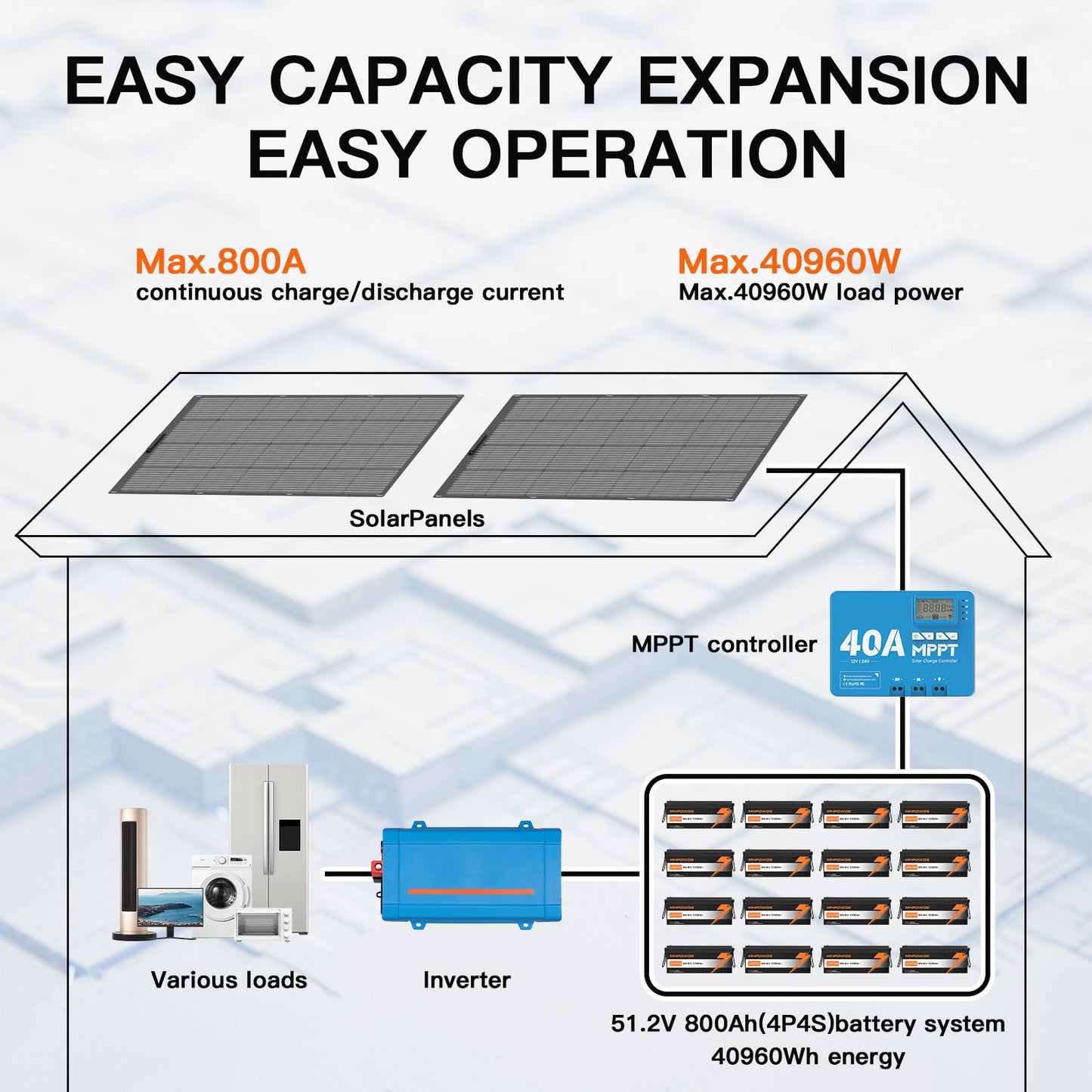
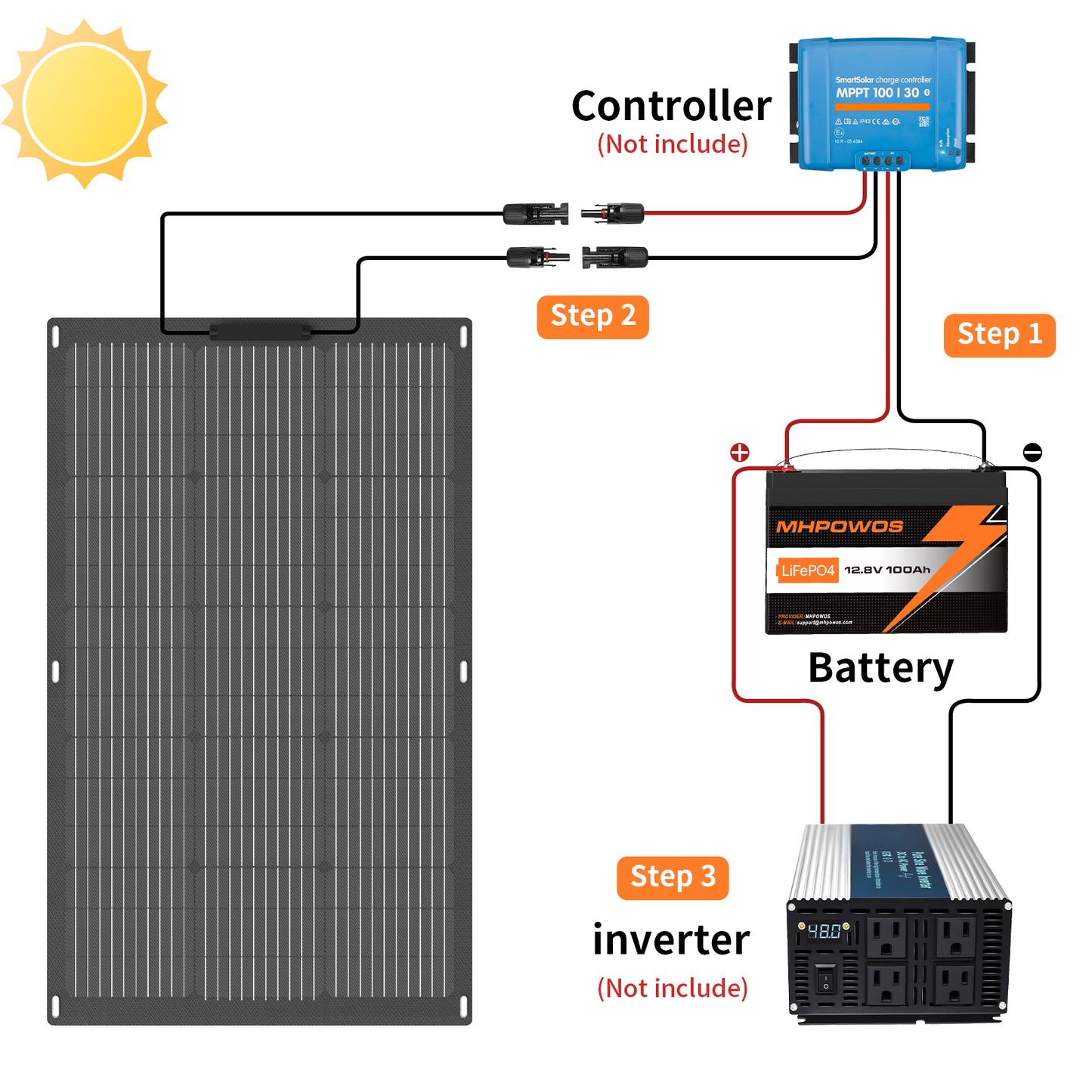
Match battery voltage (12V, 24V, etc.) to your inverter, solar charge controller and system architecture. Using mismatched voltages forces extra components and reduces efficiency.
2. Capacity & Your Energy Needs
Estimate daily usage in Wh (appliances × hours) and choose a battery that covers that usage with margin for cloudy days and system losses.
3. Depth of Discharge (DoD)
LiFePO₄ batteries tolerate deeper discharge than lead-acid. MHPOWOS batteries often allow 80–90% usable DoD, meaning more of the rated Ah is actually usable.
4. Cycle Life & Warranty
Look for the number of cycles at a stated DoD. More cycles mean a longer service life — critical for off-grid and daily-use systems.
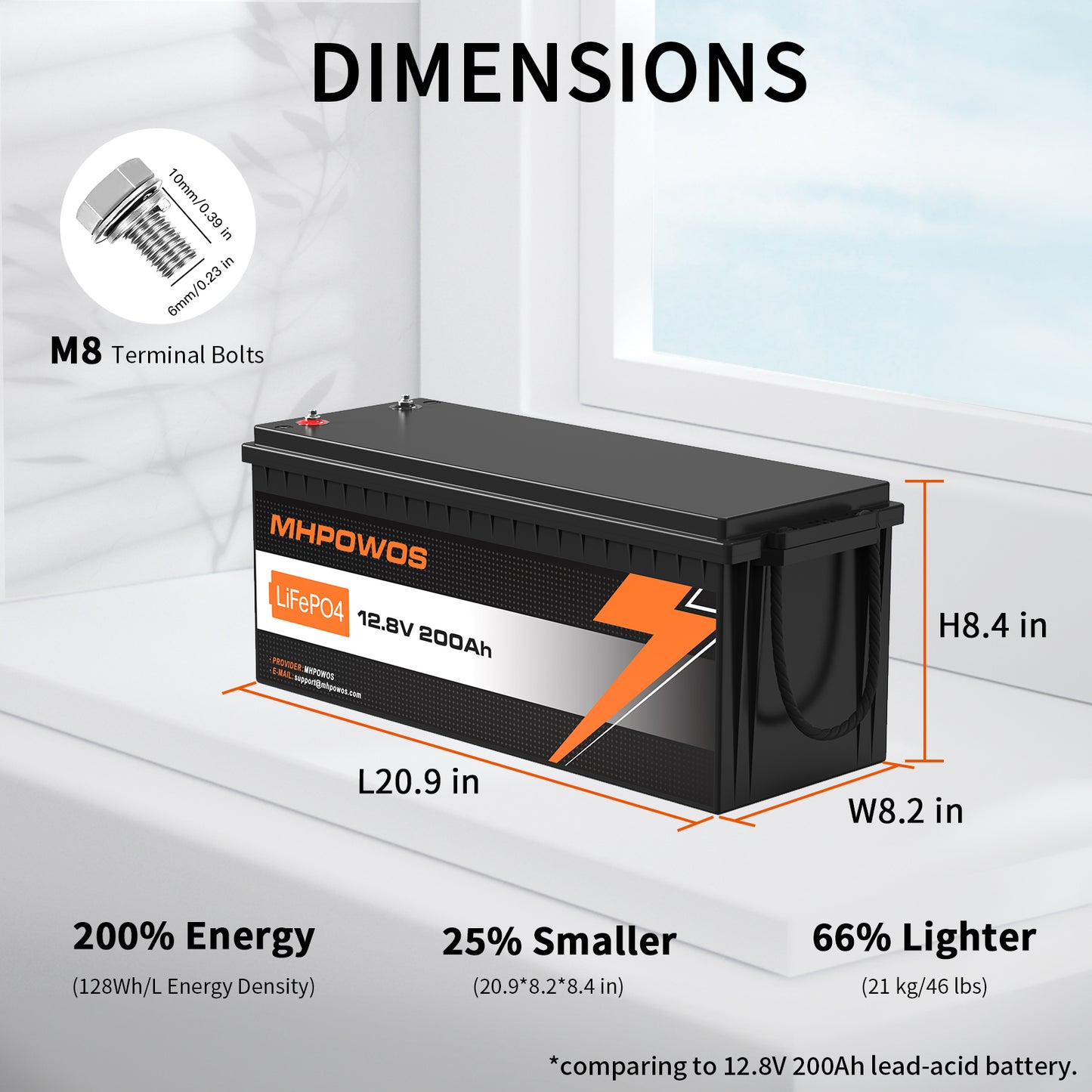
5. Size, Weight & Installation
Consider physical constraints if you’re installing in an RV or a tiny cabin. LiFePO₄ offers high energy density (more Wh per kg) than lead-acid.
6. BMS and Safety Features
A reliable Battery Management System (BMS) protects against overcharge, overdischarge, short circuits and extreme temperatures. Make sure the MHPOWOS model you choose includes or supports a BMS.
Example: Choosing a Battery for an Off-Grid Cabin
Suppose your cabin uses ~500 Wh per night (LED lights, a small fridge on low, phone charging). You want two nights of autonomy without solar input:
- Daily demand: 500 Wh
- Two nights reserve: 1,000 Wh
- Choose a battery with usable capacity ≥ 1,000 Wh. A 12.8 V, 100 Ah battery (~1,280 Wh rated) gives ~1,024–1,152 Wh usable at 80–90% DoD — a good fit.
If you prefer more margin or faster recharge cycles, step up to a larger capacity (e.g., 12.8 V, 200 Ah ≈ 2,560 Wh).
Avoid Undersizing and Oversizing
Undersizing shortens battery life because deeper discharges stress the cells. Oversizing can be wasteful if your solar array or charger cannot effectively recharge the battery each day.
Balance is key: size your battery so typical daily charging covers your average use, with extra capacity for cloudy days and unexpected demand.
Care, Installation & Maintenance Tips
- Install batteries in a ventilated, dry, and temperature-stable location.
- Use an appropriate MPPT solar charge controller to maximize charging efficiency.
- Inspect connections periodically and keep terminals clean and tight.
- Store batteries partially charged (about 40–60%) for long-term storage to protect cycle life.
- Follow MHPOWOS product manuals for charging limits, wiring diagrams, and BMS settings.
Explore MHPOWOS LiFePO₄ Battery Collection
Ready to pick a battery? Browse the complete MHPOWOS LiFePO₄ series for detailed specs, dimensions, and model comparisons:
Visit the MHPOWOS LiFePO₄ Lithium Battery Collection
(This collection includes multiple voltages and Ah ratings so you can match the exact Wh capacity you need.)
Conclusion
Understanding Ah is the first step, but always convert to Wh and consider voltage, DoD, cycle life, and system compatibility when choosing a battery. MHPOWOS LiFePO₄ batteries deliver modern performance, long life, and reliable safety features — ideal for RVs, off-grid homes, emergency backup, and mobile power systems.
Need help sizing your system? Contact MHPOWOS support or use the product pages in the collection to compare models by Ah, Wh and voltage.